Recognizing gallbladder stones: Early signs and prevention
 Why gallstone disease occurs (photo: Freepik)
Why gallstone disease occurs (photo: Freepik)
Gallstone disease can remain silent for a long time, so it's important to recognize it at early stages and start treatment immediately. Contrary to common belief, gallbladder stones don't always require surgical removal; sometimes, alternative methods can be used. Dietitian Oleg Shvets discusses why gallstones form and how to prevent them.
How often does gallstone disease occur?
"The gallbladder is located in the upper right part of the abdomen, just below the liver. It stores bile, which is released after the start of food intake and aids digestion. Issues with the gallbladder typically arise when there's an obstruction preventing the bile from exiting, such as the passage of a stone from the gallbladder into the duct," says the doctor.
Most gallstones form when substances in bile sediment, crystallize, and harden. Gallbladder stones are widespread and usually asymptomatic.
"However, about 10% of individuals diagnosed with gallstone disease experience fairly pronounced symptoms within 5 years," Shvets notes.
Signs indicating the presence of gallstones
Gallstones can cause pain in the upper right or center of the abdomen. It may occur after consuming high-fat foods, such as fried meals, but can also happen under other circumstances.
Ignoring this pain can exacerbate symptoms. The following may occur:
- fever
- rapid heartbeat
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
- itchy skin
- diarrhea
- chills
- confusion
- loss of appetite
"These symptoms can indicate an infection or inflammation of the gallbladder. However, they can also be manifestations of liver or pancreatic pathology," explains the dietitian.
As the symptoms of gallstones resemble those of other serious issues like appendicitis and pancreatitis, it's imperative to seek medical attention promptly.
"Gallstones themselves don't cause pain. Pain occurs when gallstones obstruct the flow of bile from the gallbladder. Approximately 80% of people with gallstones don't experience pain or other symptoms. In these cases, a doctor can detect gallstones in the gallbladder through ultrasound, X-rays, or during abdominal surgery," Shvets elaborates.
Why gallbladder stones form
The formation of stones is believed to stem from a chemical imbalance within the bile inside the gallbladder. This imbalance can result from:
- excess cholesterol with simultaneous suboptimal balance of bile acids in the bile, leading to the formation of yellow cholesterol stones.
- excessive bilirubin in the bile.
- concentrated bile in an overfilled gallbladder.
How this disease is diagnosed
"Initially, the doctor conducts a physical examination, which includes checking the eyes and skin for visible color changes. A yellowish hue may be a sign of jaundice, a result of excess bilirubin in the body," says the dietitian.
Other diagnostic methods include:
- Ultrasound (USG) - the best and safest visualization method to confirm the presence of gallstone disease.
- Abdominal CT scan.
- Radionuclide scanning of the gallbladder.
- Blood tests, which measure the amount of bilirubin and assess liver function.
"If gallstones in the gallbladder are asymptomatic, most likely, no action is needed. However, it's advisable to change lifestyle habits to prevent their growth and the onset of further problems," advises the doctor.
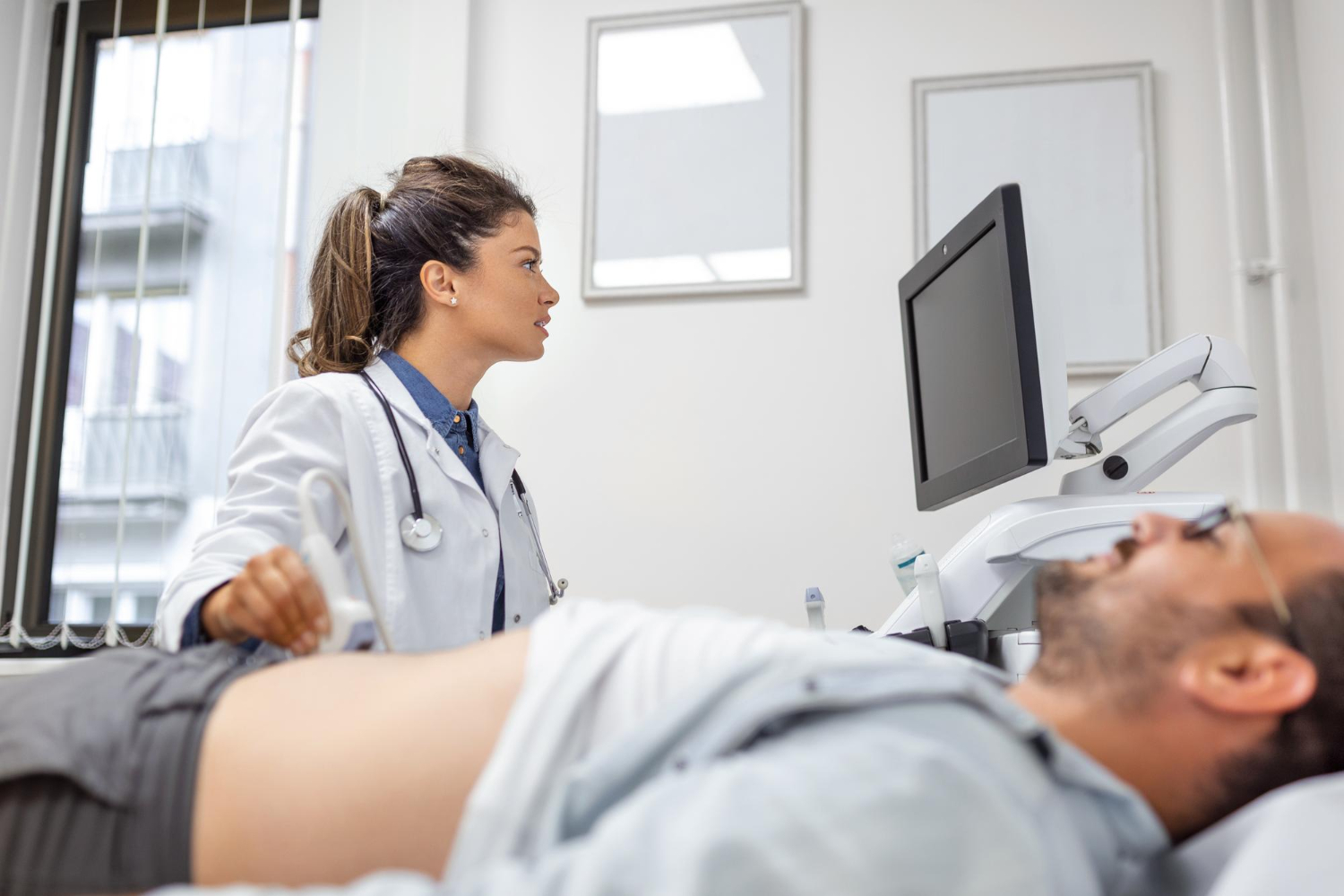 Ultrasound is the best method of confirming the presence of gallstone disease (photo: Freepik)
Ultrasound is the best method of confirming the presence of gallstone disease (photo: Freepik)
Surgical treatment methods
In most cases, if gallstones are not causing pain, they don't require treatment.
"Sometimes they can pass on their own. If there's a history of gallstone attacks, the doctor may recommend surgery. In rare cases, medications to dissolve the stones may be used. However, the downside of this treatment approach is the frequent recurrence of stones in the gallbladder," explains Shvets.
In certain circumstances, the doctor may prescribe cholecystectomy - surgery to remove the gallbladder. It can be done laparoscopically - through small incisions. If there are no complications, the patient can return home the same day or the next day.
Alternatively, the gallbladder can be removed through an open abdominal incision. This method is used if the gallbladder is inflamed, infected, or scarred.
After the organ is removed, bile from the liver is redirected to the small intestine. It becomes less concentrated. One side effect of this may be diarrhea. However, most people adapt to digestion without problems.
Non-surgical treatment methods
"If surgery is not possible, for example, if the patient is an elderly person with a high risk, there are several other ways to get rid of gallstones," says the doctor.
Non-surgical methods include:
- oral dissolution therapy usually involves the use of ursodeoxycholic acid medications, which help dissolve the stones. This treatment is best suited for breaking down cholesterol stones and may take several months or years;
- extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. A lithotriptor is a device that generates shock waves that can break gallstones into smaller pieces;
- percutaneous gallbladder drainage involves inserting a sterile needle into the gallbladder for aspiration (removal) of bile. Then, a tube is inserted for additional drainage. This procedure is typically an option for people who are not candidates for other procedures.
What causes gallstone formation
"Some factors are related to diet, while others are beyond control. Uncontrollable risk factors include age, race, gender, and family history," emphasizes Shvets.
Lifestyle risk factors:
- obesity
- type 2 diabetes
- high-fat or high-cholesterol diet and low-fiber diet
- rapid weight loss can contribute to gallstone formation
Genetic risk factors:
- female gender
- family history of gallstones
- age over 60 years
Diseases or special physiological conditions:
- cirrhosis
- pregnancy
- taking certain cholesterol-lowering medications
- taking estrogen-containing medications
"However, do not stop taking medications without a doctor's approval," advises the dietitian.
Preventing gallstone formation
"While there's no foolproof way to completely prevent gallstones, cholesterol seems to play a significant role in their formation. If you have a family history of gallstones, your doctor may advise limiting foods high in saturated fats. Specifically, fatty meats (sausage and bacon), sweets (cakes and cookies), lard, cream, and certain cheeses," says Shvets.
Since obese individuals are more prone to gallstone formation, maintaining weight within moderate limits is another way to prevent gallstone disease.
Following these rules can help reduce the risk of gallstone formation:
- Eat fewer ultra-processed carbohydrate products (such as cookies and white bread) and less sugar.
- Increase consumption of healthy fats, such as fish oil and olive oil, which help the gallbladder contract regularly and empty itself.
- Consume the recommended amount of fiber per day (about 25 grams per day for women, about 38 grams per day for men).
- Engage in physical activity daily.
- Drink enough water.
- If you plan to lose weight, do it slowly. Rapid weight loss increases the risk of gallstone formation and other health problems.
Earlier, we discussed why blood sugar fluctuations occur and how to prevent them.
Also, read about 5 steps that will help maintain the health of your liver.
This material is for informational purposes only and should not be used for medical diagnosis or self-treatment. Our goal is to provide readers with accurate information about symptoms, causes, and methods of detecting diseases. RBС-Ukraine is not responsible for any diagnoses that readers may make based on materials from the resource. We do not recommend self-treatment and advise consulting a doctor in case of any health concerns.


