Where to find 'vitamin of youth' E and why its deficiency should never be allowed
 What you need to know about vitamin E (photo: Freepik)
What you need to know about vitamin E (photo: Freepik)
Vitamin E is often referred to as the "youth vitamin" because it takes care of skin health. When lacking, the skin becomes dry and dull. It also contributes to sharp vision, muscle tone, and many other processes in the body. That's why it's essential to ensure there's no deficiency of vitamin E, but at the same time, an excess can also be harmful. Gastroenterologist Yevhenia Belinska tells what you need to know about vitamin E.
What to know about vitamin E
"Natural vitamin E exists in eight chemical forms, which have different levels of biological activity. Alpha-tocopherol is the only form that meets human needs," the doctor says.
The name tocopherol comes from the Greek words "toc" (child) and "phero" (to bear). This reflects the important role of the vitamin in the normal development of the fetus.
"Vitamin E is a fat-soluble compound that protects cell membranes from oxidation and damage. Vitamin E is not synthesized in the body. Impaired fat absorption, which may occur against the background of pathologies of the pancreas, intestines, gallbladder, and liver, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, can lead to a decrease in vitamin E intake from food," Belinska explains.
Consequences of vitamin E deficiency
"Symptoms of deficiency include visual disturbances, weakness, muscle weakness, numbness of the extremities, coordination disorders, dry skin, and pigmentation," the doctor says.
Tocopherol is stored in adipose tissue, liver, and muscles. The normal range of vitamin E in adults is 5.5-17 mcg/ml.
The daily requirement for vitamin E is 15 mg for men, women, and pregnant women. For breastfeeding mothers, it is 19 mg.
Hazards of excess
Excessive intake of vitamin E can cause diarrhea, vomiting, bloating, and increased blood pressure.
"The long-term safety of high doses of vitamin E is questionable. Data indicate a possible increase in mortality and frequency of heart failure with prolonged use of vitamin E (400 IU or more) in patients with chronic diseases," Belinska emphasizes.
According to her, high doses inhibit platelet aggregation. Two clinical studies have found an increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke in participants taking alpha-tocopherol. There is also information in scientific sources about the risk of developing prostate cancer with tocopherol intake.
Where to find vitamin E
"Nuts, seeds, and vegetable oils are some of the best sources of alpha-tocopherol, with significant amounts found in green leafy vegetables and fortified cereals," says Belinska.
Most supplements containing only vitamin E provide ≥67 mg (100 IU of natural vitamin E) of nutrient. This value significantly exceeds the daily requirement.
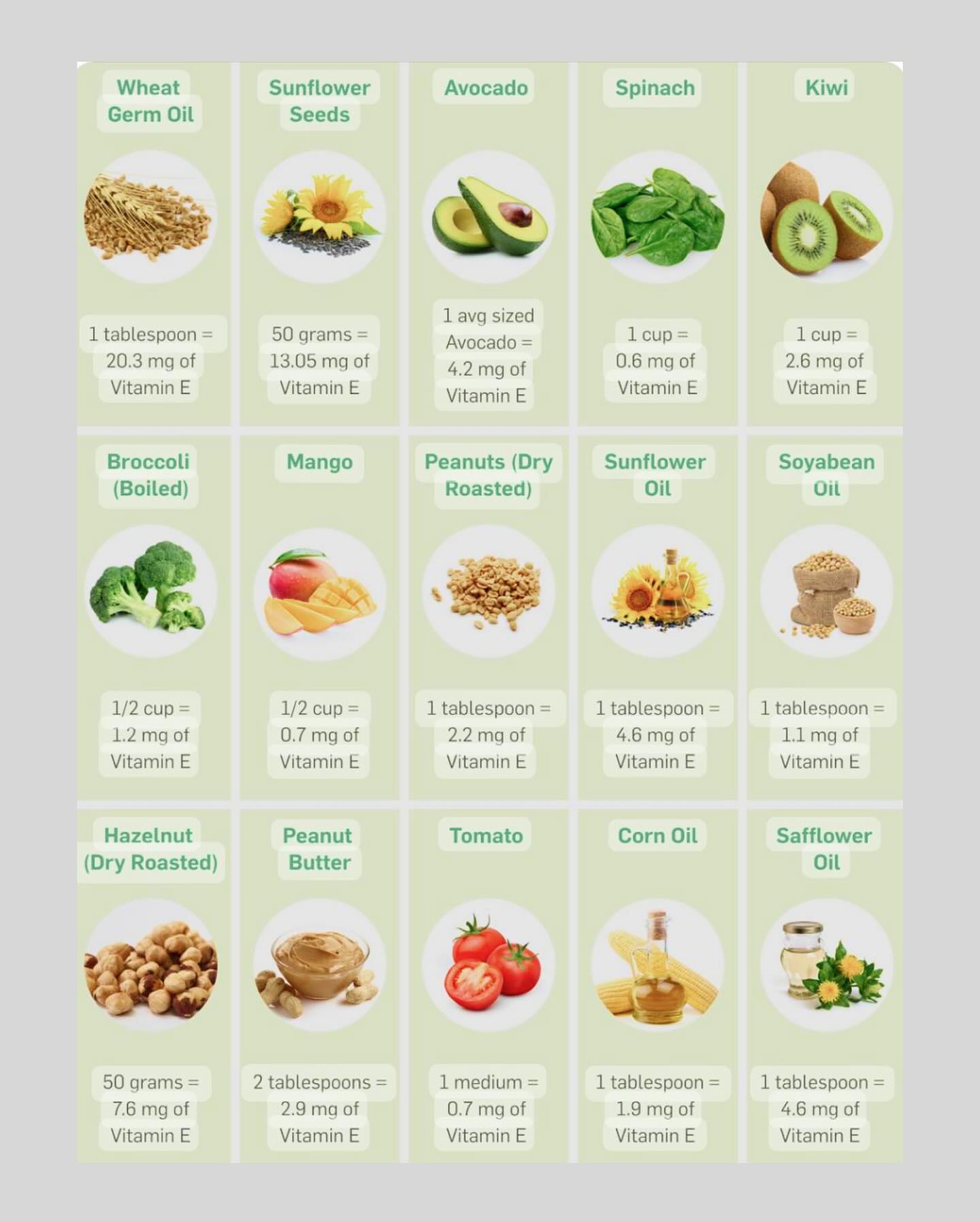 Where to look for vitamin E (photo: Instagram/dr.belinska)
Where to look for vitamin E (photo: Instagram/dr.belinska)
Interaction with medications
Vitamin E may interact with anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents, simvastatin, niacin, nutraceuticals, with tocopherol, and may also reduce the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
"Therefore, taking vitamin E should only be done under the supervision of a doctor, taking into account all the risks and potential benefits," says Belinska.
Earlier, we wrote about the 5 vitamins that women and men over 40 should take.
Also, read about the unexpected sign of vitamin D deficiency that the doctor mentioned.
This material is for informational purposes only and should not be used for medical diagnosis or self-treatment. Our goal is to provide readers with accurate information about symptoms, causes, and methods of detecting diseases. RBС-Ukraine is not responsible for any diagnoses that readers may make based on materials from the resource. We do not recommend self-treatment and advise consulting a doctor in case of any health concerns.


