Previously unknown infectious bacterium identifiied: What's known
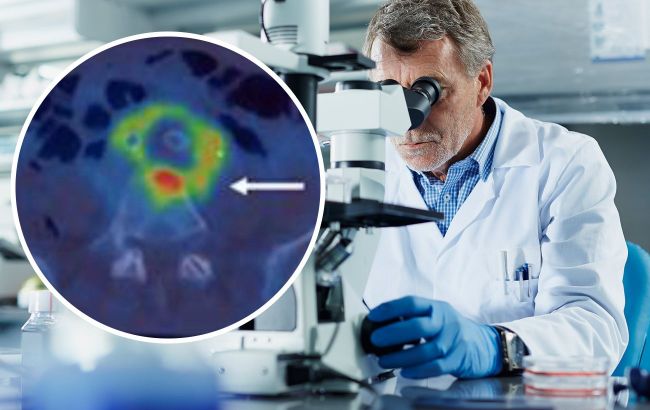 The first reported case of human infection with Variovorax durovernensis (Collage: RBC-Ukraine)
The first reported case of human infection with Variovorax durovernensis (Collage: RBC-Ukraine)
In the United Kingdom, doctors have identified an infection caused by a new strain of bacteria from the Variovorax genus, writes the journal Clinical Infection in Practice.
It is known that the infection affected a local shepherd who had a bacterial attack on the aortic stent previously implanted due to an infectious aortic aneurysm.
Details about the new bacteria
The new strain of bacteria has been named Variovorax durovernensis. The name comes from the old Latin name for the English city of Durovernum, now known as Canterbury. The first patient to be infected was a 55-year-old shepherd who looked after sheep.
Healthcare professionals and researchers from the National Health Service extensively studied this case. Initially, the patient fell ill due to the infection of the aorta with the Campylobacter fetus bacteria, leading to an aneurysm - a significant dilation of the blood vessel. Doctors inserted a stent into the aorta to correct its diameter and prescribed antibiotics.
The patient was left with an intravenous catheter through which he was supposed to administer antibiotics. Despite reducing his workload, the patient continued to have contact with sheep. He occasionally performed tasks without gloves, leading to dermatitis.
Seven months after the stent was inserted, the patient returned to the doctor. He experienced severe headaches, weight loss, frequent vomiting, and back pain. Medical examinations revealed a new infectious agent. It was speculated that the infection entered through the affected hands, becoming a gateway for the new bacteria.
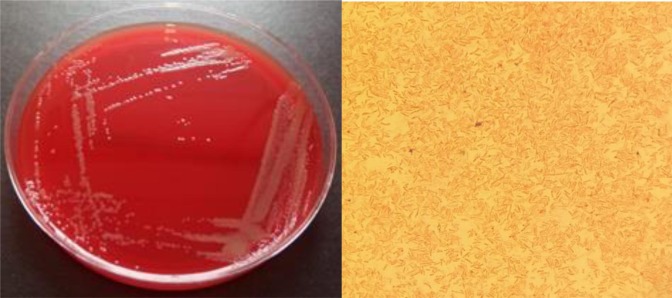
The new pathogen under the microscope (photo: sciencedirect.com)
The Variovorax durovernensis bacteria belong to a genus that typically resides in the soil. It is associated with plant root systems and plays a crucial role in the biological breakdown of organic matter in nature.
It should be noted that there is currently no information about the potential danger of this bacterium and whether it can lead to widespread infection.

