How to set up secure Wi-Fi connection on Windows
 How to configure your Windows computer to be secure when connected to Wi-Fi (illustrative photo: Freepik)
How to configure your Windows computer to be secure when connected to Wi-Fi (illustrative photo: Freepik)
Ensuring the security of your Wi-Fi connection is an absolute necessity, especially when connected to public or shared networks. Without proper protection, hackers can exploit your connection or intercept your data, reports MakeUseOf.
Change your network profile
A public profile isolates your device from others on the network, reducing the risk of hackers compromising your connection. In contrast, a private profile makes your device visible, allowing data to be exchanged with other users.
Data sharing can be helpful for home networks where you trust all connected users, but it also increases vulnerability, enabling others to send and receive data from your device.
Due to the risks it creates, a private profile should only be used in secure home networks. It is better to switch to a public profile when connecting to unreliable networks in public places, such as cafes or airports.
To change your network profile, go to Settings, Network & Internet, Wi-Fi, and click on Manage known networks. Select the network you're connected to and click on the desired profile.
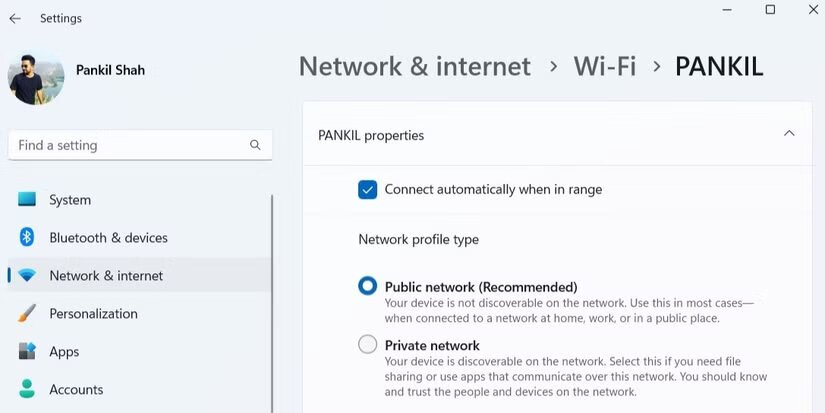
Change your network profile (photo: MakeUseOf)
Disable automatic connections to open networks
Windows automatically connects to previously used Wi-Fi networks when they are within range. While convenient, this can also be a serious security risk.
You may inadvertently connect to a public network you used before, which may already be compromised. To enhance security, you should turn off automatic connections to old networks and forget public networks after use.
To stop automatic connections, click on the Wi-Fi icon in the system tray and select the network. Then uncheck the Connect automatically option.
To forget a saved Wi-Fi network, open Settings, Network & Internet, Wi-Fi, and Manage known networks. Find the network you want to remove and click Forget.
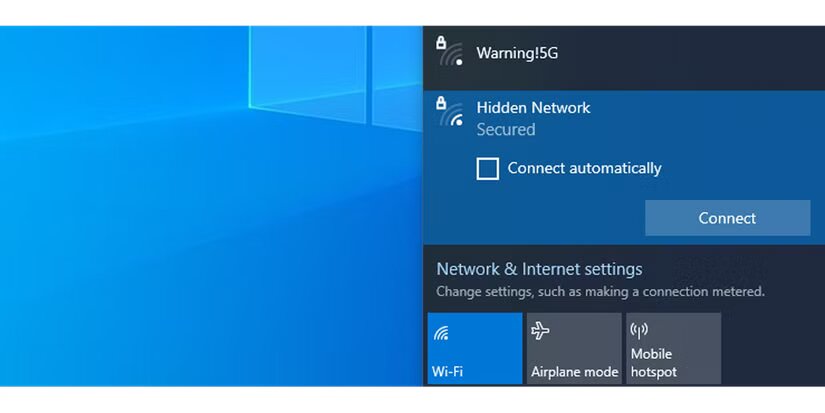
Disable automatic connections to open networks (photo: MakeUseOf)
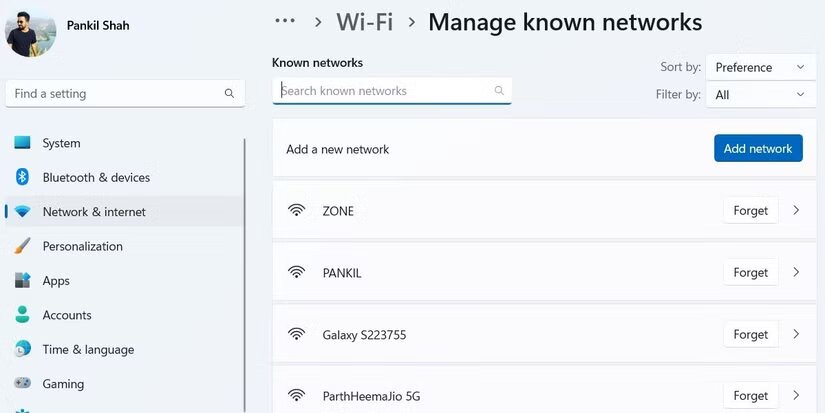
Disable automatic connections to open networks (photo: MakeUseOf)
Enable random hardware addresses
When your computer searches for Wi-Fi networks, it sends a unique hardware (MAC) address associated with your device. Cybercriminals can use this information to track your location.
To protect your privacy, enable random hardware addresses. This generates a new MAC address every time you connect to a network.
To enable random hardware addresses for all networks, go to Settings, Network & Internet, Wi-Fi. Then enable the Random hardware addresses option.
To enable random hardware addresses for a specific network, go to Manage known networks, select the desired network, and turn on the Random hardware address option.
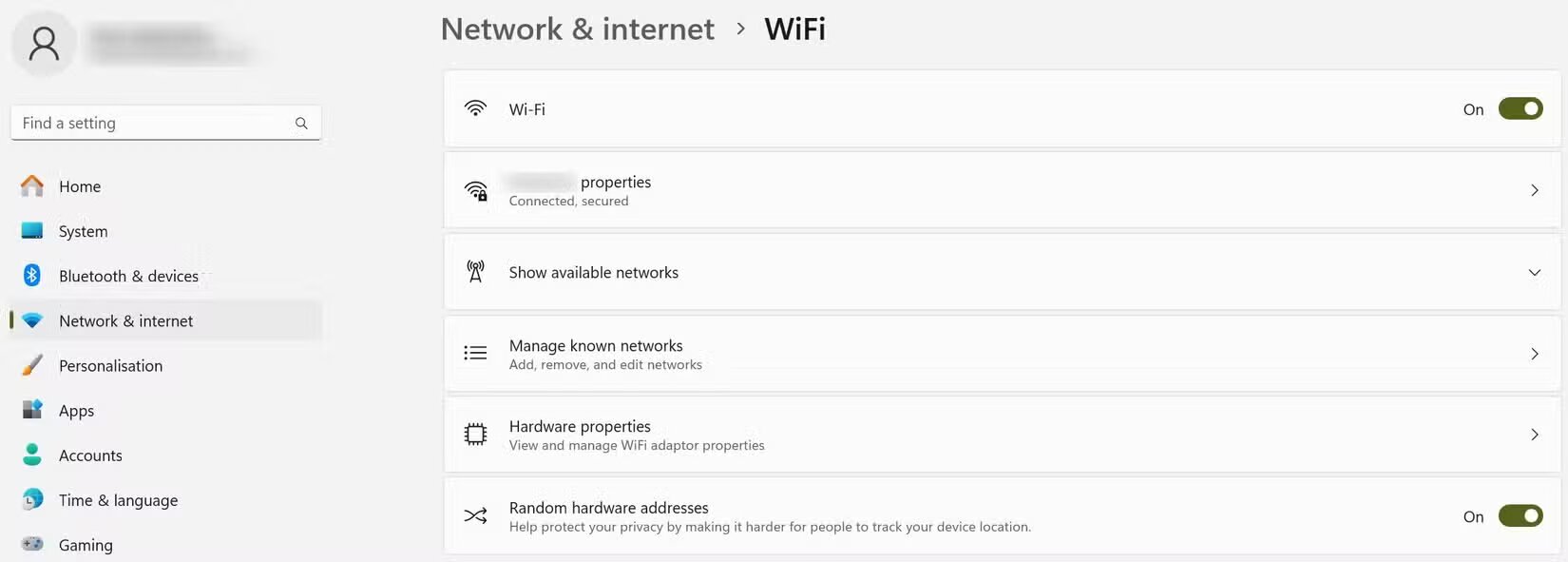
Enable random hardware addresses (photo: MakeUseOf)
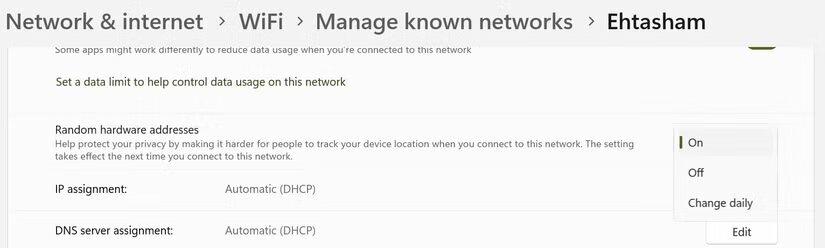
Enable random hardware addresses (photo: MakeUseOf)
Set automatic IP network settings (DHCP)
You can assign an IP address to your device in two ways: automatically (via DHCP) or manually (using a static IP).
With DHCP, your router or network assigns an IP address to your device every time it connects to the network. This is sometimes called a dynamic IP. A manually assigned (static) IP address allows you to set a fixed IP for your device.
DHCP improves security by periodically changing the IP address, making it ideal for use in public or unreliable networks.
To enable dynamic IP address assignment, follow these steps:
- Go to Settings, Network & Internet, and Wi-Fi.
- Click on
for the active connection, then scroll to the IP assignment section. - Click Change, select Automatic (DHCP) from the menu, and save the changes.
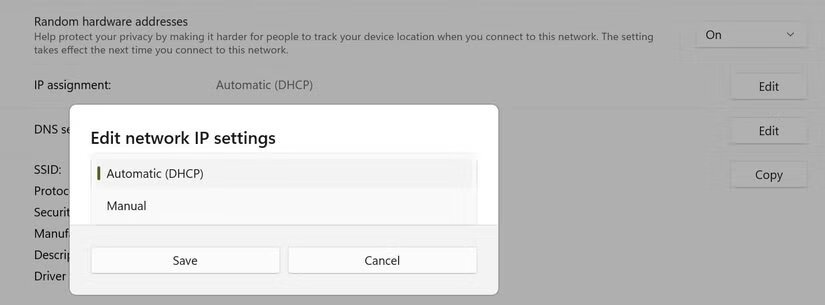
Set automatic IP network settings (DHCP) (photo: MakeUseOf)
Change encryption protocol
Your Wi-Fi network should use modern encryption standards, ideally WPA3 or at least WPA2, to protect your data from unauthorized access.
While encryption settings are managed through your router’s interface, Windows allows you to check which encryption protocol your network is using easily.
To check your security protocol:
- Go to Settings, Network & Internet, Wi-Fi.
- Open your connected network and check the protocol listed next to the security type.
If your network uses an outdated encryption protocol, you should update your settings:
- Open a web browser and enter your router’s IP address in the address bar.
- Log in using your router’s administrative credentials.
- Go to Wireless Settings or Wi-Fi Settings.
- Find the encryption option and select the strongest available protocol, such as WPA3 or WPA2.
These are essential steps to secure your Wi-Fi connection. Also, make sure your network is protected with a strong, hard-to-guess password, and avoid sharing it with outsiders.
Many routers allow you to create a guest network for visitors, which helps maintain the security of your connection.
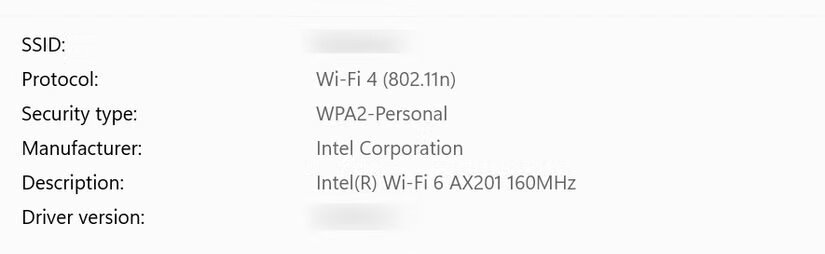
Change encryption protocol (photo: MakeUseOf)
Lastly, Microsoft simplifies file sharing between iPhones and Windows devices.

