Giant volcano found on Mars: Potential for hidden water reserves
 Giant volcano found on Mars (photo: Unsplash)
Giant volcano found on Mars (photo: Unsplash)
It seems that an object as tall as 9 kilometers could not remain unnoticed even on a planetary scale. However, for many years, scientists overlooked a volcano on Mars despite active research. The combination of data obtained by various orbital devices allowed for this remarkable discovery, according to the SETI Institute.
What is known about the found volcano
For a long time, a volcano known as Noctis Mons was hidden in the Noctis Labyrinthus region, thanks to its densely cracked and canyon-covered terrain, which served as natural camouflage. This volcano is now heavily eroded, being in a severely ruined state.
With its height of 9,022 meters (29,600 feet), Noctis Mons ranks seventh among objects on Mars by height. This significantly surpasses Earth's highest dormant volcano, which is only 6,893 meters tall.
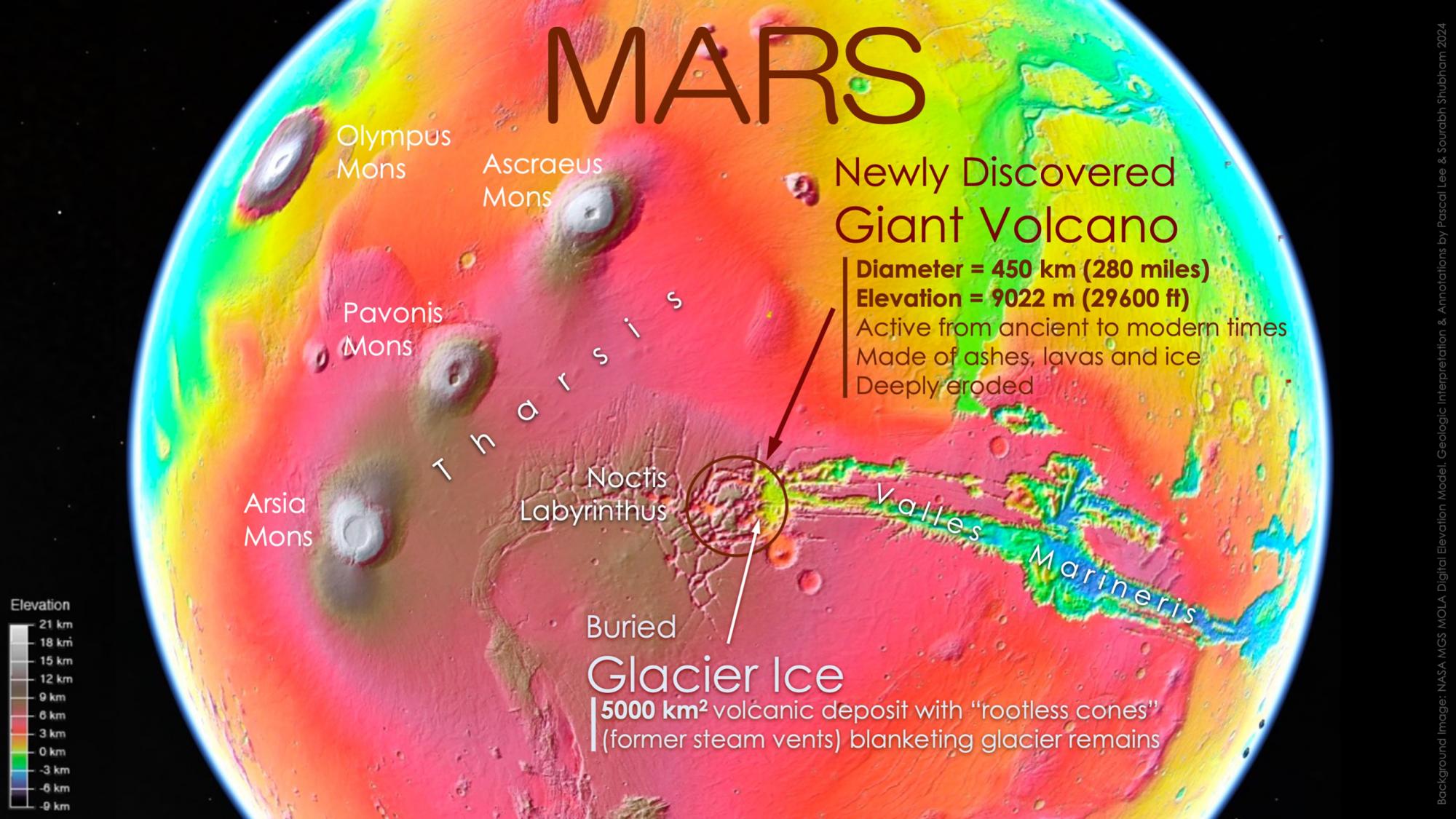 The height of the volcano is 9,022 meters (photo: SETI)
The height of the volcano is 9,022 meters (photo: SETI)
Past volcanic activity in the Noctis Labyrinthus region hinted at the presence of water through the minerals found there, formed from volcanic rocks in the presence of water. It offers additional interest and prospects for future research.
Determining the location of Noctis Mons was possible thanks to the terrain's structure. Remnants of a caldera, a crater once filled with lava, remain at the center of the region. The area of volcanic deposits is approximately 5 thousand square kilometers.
The size of the volcano and the complexity of the surrounding terrain suggest that it was active for a long time. Near the base of one of its sides, researchers found deposits formed after lava covered a water and ice-rich surface. It indicates that there might have been a glacier at this location during the volcano's active period.
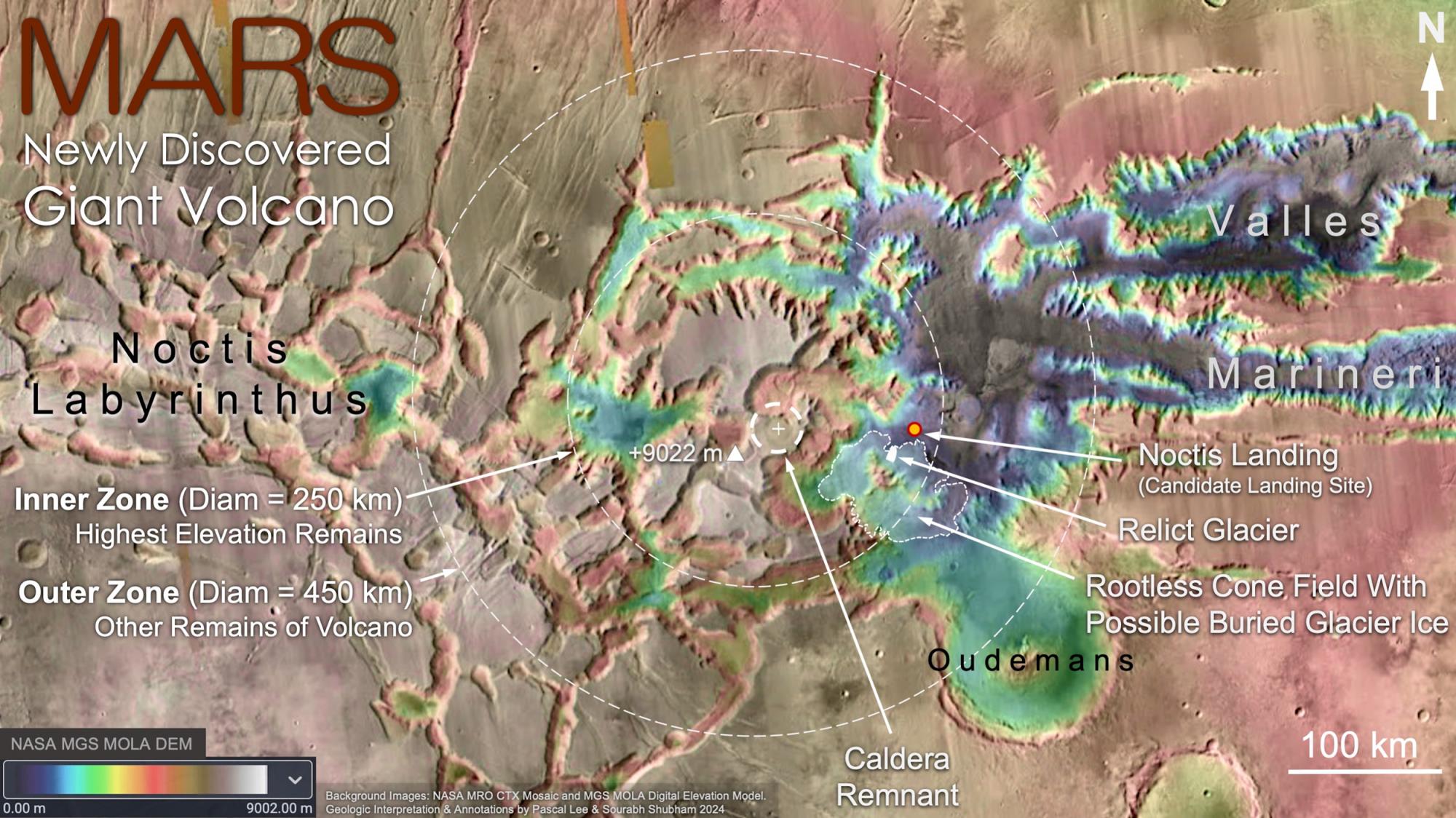 The volcano was destroyed over prolonged erosion (photo: SETI)
The volcano was destroyed over prolonged erosion (photo: SETI)
Conclusions
Researchers speculate that residual traces of a glacier, i.e., frozen water reserves, may remain beneath the region's surface. If Noctis Mons still retains internal heat, then theoretically, conditions for supporting life could exist in the depths of Noctis Labyrinthus. Previous studies indicate that Mars maintains seismic and geological activity.
Check out also how Mars could affect Earth's climate and the discovery of lake remnants on Mars.

