'Heat dome': What is known about this weather phenomenon and how it poses threat to humanity
 Global warming affects various processes (photo: Getty Images)
Global warming affects various processes (photo: Getty Images)
Scientists warn Earth residents about the need to adapt to the formation of a so-called "heat dome" in certain regions.
RBC-Ukraine reports on what should be known about this phenomenon, what it may depend on, and whether it poses a threat to humanity.
What is a 'heat dome'
A "heat dome" is a meteorological phenomenon increasingly associated with global warming. It involves the formation in the atmosphere of a limited area of hot oceanic air with stable weather conditions in the upper layers (known as an Omega block).
In this scenario, high pressure prevents cooler air from penetrating into the dome. Instead, warm air, in conditions of reduced circulation and humidity, accumulates in the atmosphere and descends to the surface.
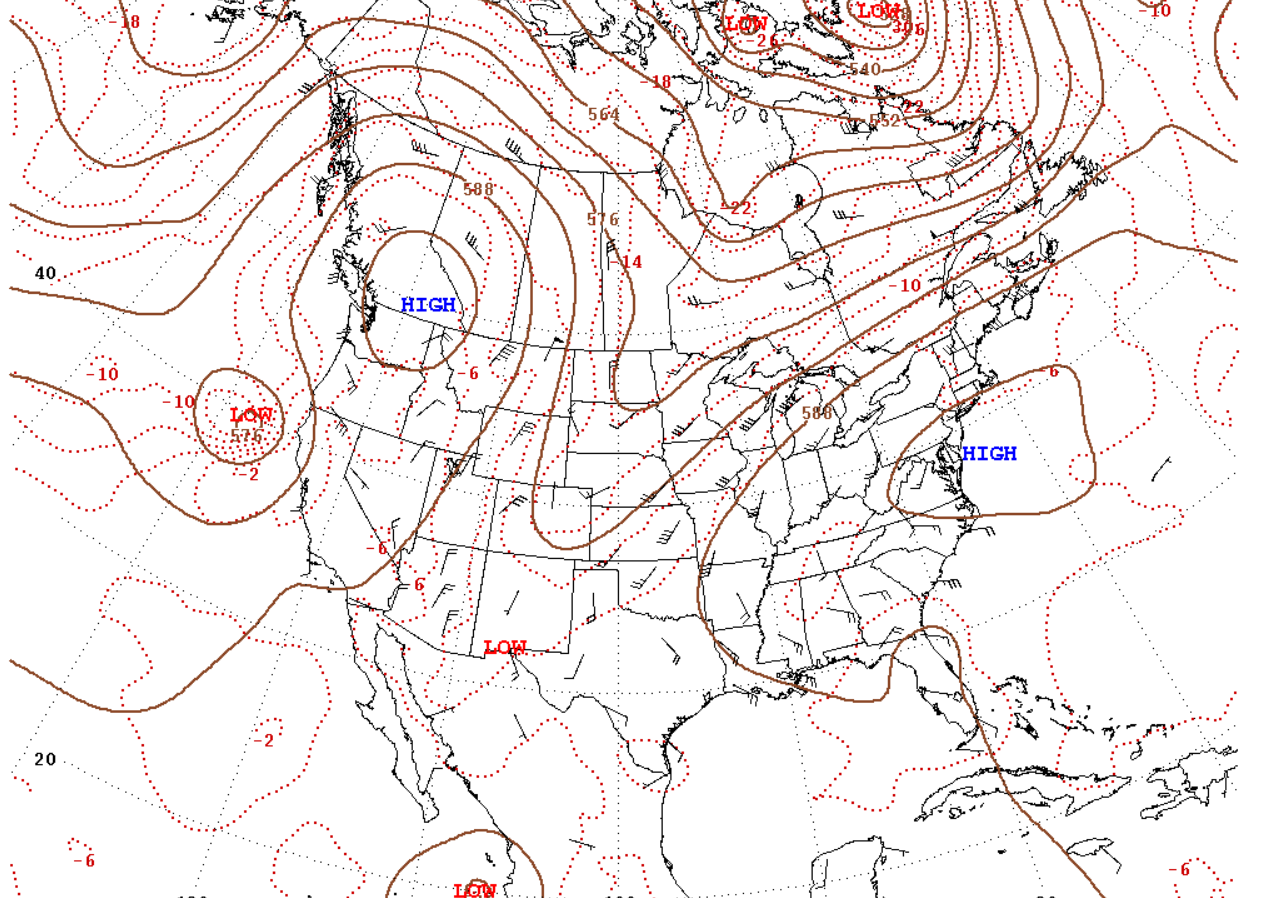
Example of the dominance of high pressure (illustration: en.wikipedia.org)
There the air compresses and heats up even more, but when it tries to rise, the high pressure forces it back down.
Some researchers note that this process resembles water boiling in a pot with a closed lid.
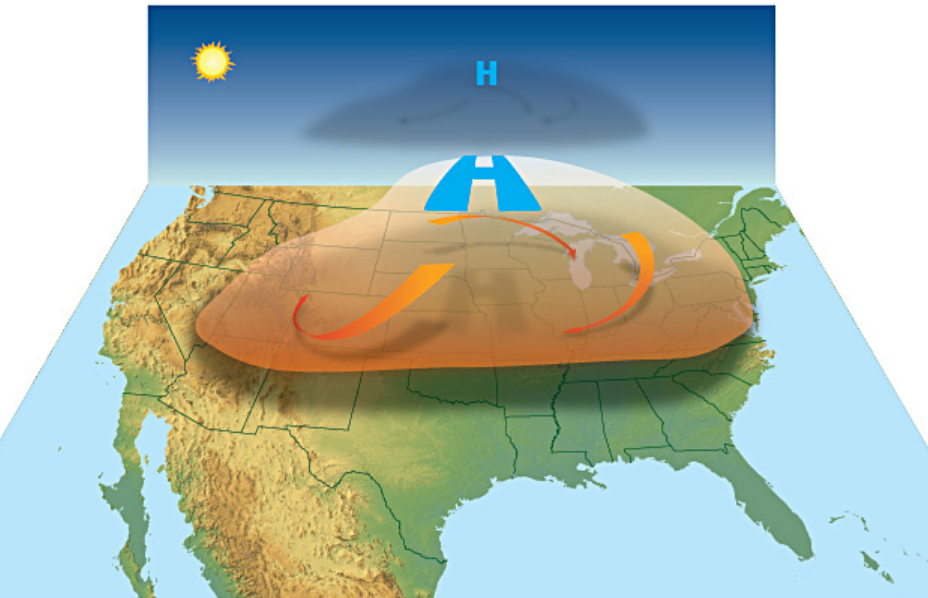
"Heat dome" over the USA (illustration: en.wikipedia.org)
According to Marc Chenard, a meteorologist with the National Weather Service (NWS) in the USA, humanity should get used to the phrase "heat dome," as it's quite likely that we will experience periodic episodes of excessive heat.
What can influence the formation of a 'heat dome'
According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), "heat domes" are likely to form most frequently in North America, especially during the La Niña phenomenon in the Pacific Ocean, which is characterized by below-normal surface water temperatures in the eastern tropical zone.
This can be explained by the temperature difference between the eastern and western parts of the Pacific Ocean, where winds push hot air eastward towards North America.
According to the majority of researchers, global warming on the planet makes such heat waves hotter, longer-lasting, larger in scale, and more frequent.
Is the 'heat dome' a threat to humanity
The "heat dome" has been observed by scientists on multiple occasions and is characterized by a sharp increase in temperature, resulting in millions suffering from heat waves.
Experts note that anthropogenic climate change (caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, sulfates, dust, and other industrial waste in the atmosphere) affects heatwaves, a scientific fact. What was once a rare occurrence is now becoming more common.
Therefore, humanity will likely have to adapt to periodic heatwaves, though global catastrophe is not currently imminent.
Sources: IFLScience, AccuWeather, Wikipedia.

