Explainer: What are swing states and their key role in US presidential election
 Donald Trump and Joe Biden at the debate (photo: Getty Images)
Donald Trump and Joe Biden at the debate (photo: Getty Images)
Both candidates of the US presidential election are particularly actively agitating in the swing states. The results of voting in these states determine the outcomes of the presidential election.
RBC-Ukraine explains the specifics of this year's swing states and their role in the 2024 election.
The United States holds presidential elections according to a specific scheme compared to other countries. Formally, the president is not elected directly by the population, but by an electoral college, the number of which varies from state to state, depending on the population.
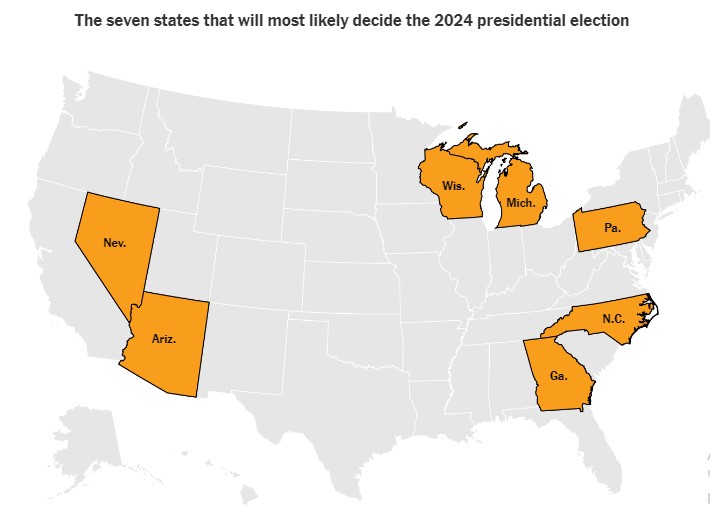
In most states, elections are held on a winner-take-all basis. So to become the US president, the candidate needs to win in individual states. Most states traditionally vote either for Democrats or Republicans. But there are so-called swing states, where candidates from both parties have roughly equal chances of winning. 270 electoral votes are needed to become president of the United States. The 7 swing states together have 93 votes - more than enough to tip the scales either in favor of Joe Biden or Donald Trump.
According to most polls, Trump holds the lead in swing states - but, as a rule, the gap is comparable to the level of statistical error.
Arizona (11 electoral votes)
Located in the southwest of the US, near California, this state has long been considered reliably red, meaning it supported Republicans in elections. Everything changed in the 2020 presidential election when Biden won the state with a minimum margin of 0.3%.
Arizona borders Mexico, so it was particularly affected by the migration crisis. Therefore, the state became the center of the national debate on immigration. This situation arose during Biden's term in office, which turned a large number of voters against him. Yet, about a third of the state's population is Latino. They are generally more likely to support Biden, but Trump is also trying to win their support by appealing to traditional Catholic values.
Georgia (16 electoral votes)
A state in the southeastern of the US near Florida, Georgia, was considered a Republican state until 2020, when Biden won there, as well as in Arizona, with a minimum margin of 0.25% of the vote. According to polls, the main concern of the population of Georgia is inflation and the rising cost of living.
In Georgia, the share of African Americans among the population is 33%. It is believed that this demographic group contributed to Biden turning the state in 2020. However, according to polls, many black voters feel disappointed that Biden has not done enough to fight racial injustice and improve the economy.
Michigan (15 electoral votes)
A state in the north-central part of the United States, in the Great Lakes region. It has traditionally been a Democratic stronghold, supporting their candidates between 1992 and 2012. But in 2016, the population of Michigan unexpectedly favored Trump. He succeeded by appealing to white working-class voters, especially in rural areas and former industrial centers. Trump promised to revive manufacturing jobs and renegotiate trade agreements. But already in 2020, voters' sympathies returned to Biden.
Michigan has the largest share of Arab Americans in the United States, a demographic that is particularly sensitive to Biden's support for Israel amid the military operation in Gaza. So this time, they may lean toward Trump.
Nevada (6 electoral votes)
A sparsely populated state with deserts and mountains, a home to Las Vegas. In the last few elections, it supported the Democrats. But the situation is changing.
The main problem in Nevada is the economic recovery, which has been slower than elsewhere in the United States after the coronavirus pandemic. The state has the highest unemployment rate in the country, after California and the District of Columbia.
Map of swing states in the United States (photo: nytimes.com)
Immigration is the second most important issue in the polls. 30% of Nevada's population is Latino. For this group of voters, the main struggle is taking place.
Pennsylvania (19 electoral votes)
A state in the northeastern United States. In 2016, Trump won there by a narrow margin of 0.5%. But four years later, Biden won with a margin of just over 1%.
The state is one of the most divided in terms of socioeconomic structure. In the southeast and west are the large cities of Philadelphia and Pittsburgh, where Democrats dominate. The rest of the territory is predominantly rural and dominated by Republicans. So white working-class voters are a key constituency for both candidates. As in many other states, people are most concerned about the economy, abortion, and immigration.
In Pennsylvania, Trump's former rival in the primaries, Nikki Haley, has a strong position. She received 16% of the vote, even though she withdrew from the primaries. Therefore, Nikki Haley's public support could give Trump an advantage.
Wisconsin (10 electoral votes)
A state in the north-central part of the United States above Lake Superior and Lake Michigan. Almost 80% of voters in Wisconsin are white. As in Michigan, a recent years decline in industrial production has led to an upsurge in unemployment, which increases the number of Trump supporters.
From 1988 to 2012, Democrats won in Wisconsin, but in the 2000 and 2004 elections, the winner's margin of victory was only 2% and 4%, respectively. In the 2016 election, Trump took over the state, but in 2020 the situation reversed. And in this year's election, the situation remains unpredictable.
North Carolina (16 electoral votes)
A state in the eastern United States that combines the Atlantic lowlands and the Appalachian Mountains. It regularly changes its winners. About 62% of North Carolina's population is non-Hispanic white. The state also has a notable share of African Americans - 22.2%. The problems that concern voters are primarily related to the economy and rising housing costs.
Earlier, RBC-Ukraine explained the political implications of the attempted assassination of Donald Trump.
Sources: results of the previous US elections, opinion polls, and American media.



