Scientists estimate timeline for ozone hole’s complete healing
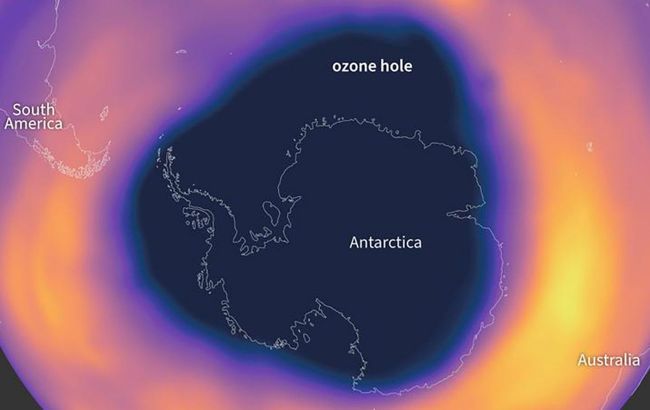 The ozone hole has become the smallest in recent years (photo: NOAA)
The ozone hole has become the smallest in recent years (photo: NOAA)
Research on the ozone hole over Antarctica showed that its size this year had reached the seventh smallest level since 1992, when the Montreal Protocol came into effect, according to TVN24.
Role of Earth’s ozone layer
The ozone layer acts as a planetary solar filter. The region of higher ozone concentration in the stratosphere protects us from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. In the second half of the 20th century, human activity caused a sharp increase in the phenomenon of ozone holes, vast areas where ozone concentration is extremely low.
Studies showed the negative impact of CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), chemicals used in refrigerators, packaging, and aerosols. These chemicals react with atmospheric ozone, decreasing its concentration. By the mid-1980s, the ozone layer had been so depleted that by early October each year, a significant portion of the Antarctic stratosphere was almost completely devoid of ozone.
Ozone hole becomes the smallest in five years
In 1987, an international agreement was reached to phase out products and processes based on chlorofluorocarbons gradually. Real action under the Montreal Protocol began in 1992. Since then, scientists have observed a gradual reduction in the ozone hole.
Recent studies have shown that this year, its size ranked as the seventh smallest in the past 22 years. On September 28, it reached its maximum size of 22.4 million square kilometers, more than twice the total area of the United States. The last time a smaller ozone hole was observed was five years ago.
Scientists say that this year’s improvement is the result of a combination of decreased concentrations of ozone-depleting substances, which were halted following the Montreal Protocol, and an unexpected influx of ozone carried by air currents near northern Antarctica.
“The 2024 Antarctic hole is smaller than ozone holes seen in the early 2000s,” said Paul Newman, leader of NASA’s ozone research team and chief scientist for Earth sciences at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. According to the expert, the current state of the ozone layer over the Southern Hemisphere shows that international efforts to reduce the use of ozone-depleting chemicals are yielding positive results.
When the ozone layer “heals”
Although the Montreal Protocol has significantly reduced harmful CFC emissions, compounds released many years ago remain in the atmosphere. Experts believe their breakdown will take many years.
"For 2024, we can see that the ozone hole's severity is below average compared to other years in the past three decades, but the ozone layer is still far from being fully healed,” said Stephen Montzka, senior scientist with NOAA's Global Monitoring Laboratory. Researchers estimate that the ozone layer will fully recover by 2066.
In addition, read about the 5 most surprising findings in Antarctica that amazed scientists.
We also have an article on how air pollution affects digestion.


